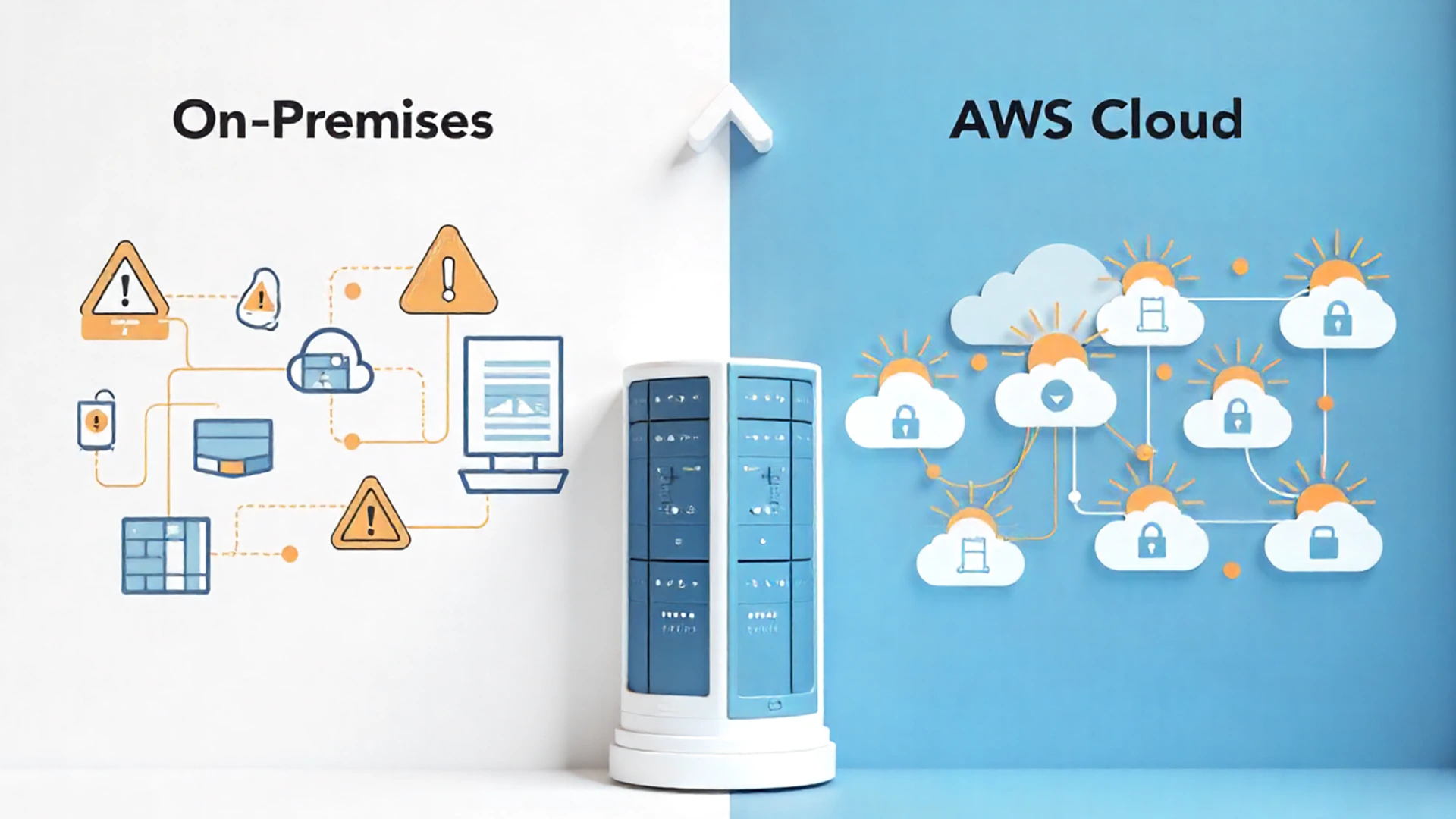
Seamless Migration: How to Successfully Move from On-Premises to AWS
Migrating from on-premises infrastructure to AWS is a transformative step for businesses looking to scale efficiently, reduce costs, and enhance security. However, successful migration requires a strategic approach that ensures minimal disruption, optimal resource utilization, and long-term cost efficiency. This blog explores a structured approach to AWS migration, best practices, and key challenges organizations must address.
Why migrate to AWS?
Organizations move to AWS for several compelling reasons:
- Scalability: AWS allows businesses to scale resources on-demand without the need for expensive hardware upgrades.Cost optimization: With pay-as-you-go pricing, organizations can reduce capital expenditures and pay only for the resources they use.
- Security & compliance: AWS provides robust security features, including encryption, IAM policies, and compliance with industry standards like ISO 27001 and GDPR.
- Innovation & agility: AWS offers cutting-edge services in AI, ML, big data, and IoT, enabling businesses to innovate faster.
- Reliability: AWS’s global infrastructure ensures high availability and disaster recovery capabilities to minimize downtime.
The AWS migration framework
AWS provides a structured approach to migration through the AWS Migration Acceleration Program (MAP), which consists of three key phases:
1. Assessment & planning
Before migration, businesses must assess their current environment and define their migration strategy. This phase includes:
- Workload discovery: Identifying applications, databases, and dependencies that need migration.
- Cost analysis: Estimating costs using AWS Pricing Calculator and Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) tools.
- Choosing the right migration strategy: AWS suggests six strategies, known as the 6 R’s of migration:
- Rehost (Lift and Shift): Moving applications as-is to AWS without modification.
- Replatform: Making minimal modifications to optimize for AWS.
- Refactor: Rewriting applications to take full advantage of AWS-native services.
- Repurchase: Moving to a different SaaS or PaaS solution on AWS.
- Retire: Decommissioning redundant applications.
- Retain: Keeping some workloads on-premises if necessary.
- Risk assessment: Identifying potential challenges such as downtime, data consistency, and security compliance.
- Stakeholder alignment: Engaging IT teams and leadership to ensure smooth coordination.
2. Migration execution
Once a migration plan is in place, the next step is execution. This involves moving workloads to AWS while ensuring minimal service disruptions. Key steps include:
- Data migration: Transferring data using AWS DataSync, AWS Snowball, or AWS Direct Connect for large-scale migrations.
- Application migration: Using AWS Migration Hub to track progress and streamline application transfers.
- Database migration: Leveraging AWS Database Migration Service (DMS) to migrate databases with minimal downtime.
- Security & compliance: Ensuring secure authentication, encryption, and compliance adherence during migration.
- Testing & validation: Verifying that applications function correctly in the AWS environment before full deployment.
3. Optimization & modernization
After migration, businesses must optimize their cloud environment to maximize performance and cost savings. Key areas include:
- Right-sizing resources: Adjusting EC2 instances, storage, and networking configurations to align with actual usage patterns.
- Auto-scaling & load balancing: Implementing AWS Auto Scaling and Elastic Load Balancing to optimize performance under varying loads.
- Cost management: Utilizing AWS Cost Explorer, Savings Plans, and Reserved Instances to minimize expenses.
- Security best practices: Enforcing IAM policies, multi-factor authentication, and continuous monitoring with AWS Security Hub.
- Automation & DevOps: Using AWS Lambda, AWS CloudFormation, and CI/CD pipelines to streamline operations.
Overcoming migration challenges
Despite the benefits, AWS migration comes with challenges. Businesses should prepare for:
Downtime risks
- Solution: Implement phased migration and failover strategies to minimize disruptions.
Compatibility issues
- Solution: Conduct pre-migration assessments to identify dependencies and refactor applications accordingly.
Cost overruns
- Solution: Continuously monitor and adjust resources using AWS Cost Management tools to prevent overspending.
Skill gaps
- Solution: Invest in AWS training and certification programs for IT teams to enhance cloud expertise.
Conclusion
Migrating to AWS is a game-changer for businesses seeking scalability, cost savings, and innovation. However, successful migration requires careful assessment, a strategic execution plan, and continuous optimization. Organizations that follow best practices and leverage AWS tools can ensure a seamless and efficient migration experience.
Are you ready to migrate to AWS? Contact Insoft Services today for expert guidance and end-to-end migration support!
 Finland
Finland Germany
Germany Denmark
Denmark Sweden
Sweden Italy
Italy Netherlands
Netherlands Norway
Norway 

























No Comments