SDWAN in a Multi-Domain Architecture

What is a Dedicated Internet Access (DIA) circuit?
A Software Defined Wide Area Networking solution using SD-WAN technology and dedicated internet access circuits is ideal.
A Dedicated Internet Access service is an Internet access service delivered over a carrier-grade network. This is the same type of network telecom service providers use to make fast, reliable Internet connections available on a large scale to customers.
With Dedicated Internet Access, you also get the same performance and quality of connectivity for your organization. Based on the carrier-grade network, the following features are available:
● Minimum round-trip time
● Minimum packet loss
● Low latency
The local network is fully redundant and uses a mesh topology, which means its spread over a large number of access points. Therefore, if something does go wrong with one access point, network traffic will simply move to the next one. Furthermore, the international network uses undersea fibre optic cable systems, and there’s monitoring of the capacity of all links 24/7 to provide a continuous Internet service.
A Dedicated Internet Access (DIA) circuit is a cost effective dedicated 1:1 Internet Service that includes the following:
● 28 Public IP ranges per circuit
● The DIA service is configured with various bandwidth guarantees.
● The full allocation of the maximum bandwidth (1:1) is received under normal conditions for local and international traffic
● The service is symmetrical (for example: 100Mbps up and down)
● There are no data caps
The bandwidth for all the SD-WAN sites will be at least double the current bandwidth, with dual diverse Dedicated Internet Access links forwarding traffic based on policies as defined by enterprises. Should a link fail (A or B link), a failure policy would ensure that all applications are routed through the diverse available link, with all critical traffic prioritised based on business rules.
Cisco SD-WAN:
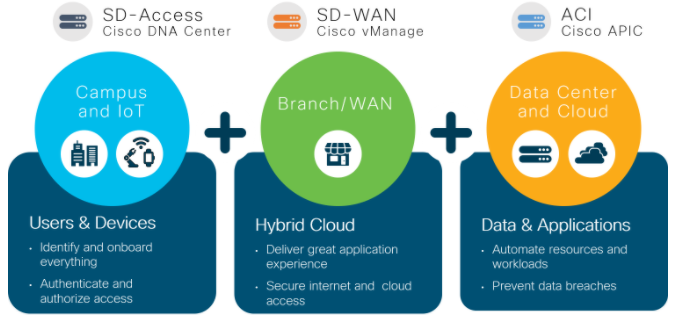
Cisco SD-WAN is one of the SDWAN leaders, this is part of Cisco’s multi-domain strategy where application requirements, user experiences, and segmentation policies can now be translated and applied to the Campus Access, Wide Area networking, and Data Centre domains.
For an enterprise with an install base of Cisco SD-Access equipment and a Cisco Software Defined Data Centre utilising ACI. Adding Cisco SDWAN will provide all the components for a Cisco multi-domain architecture to provide policy integration, while each Domain is able to function independently. Therefore, the enterprise would be in a position to apply a policy once and apply it everywhere, from the Campus Access, through the Wide Area Network and into the Data Centre to ensure the realisation of a business intent based on defined policies.
Towards an Intent-Based Architecture
Cisco is taking steps to stitch the SD-Access Campus, SD-WAN and Data Centre domains together by sharing policy elements so that each domain can cooperate with each other to fulfill the collective intent. Therefore, the new policy integrations will provide complete end-to-end network segmentation, application experience, and security.
Segmenting Policy Integrations
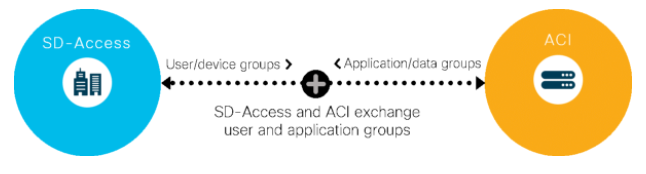
Segmenting a network reduces congestion, improves security and compliance, and fixes network problems. In the campus, Cisco’s SD-Access solution uses this technology to group users and devices within the segments it creates according to their access privileges. Similarly, Cisco ACI creates groups of similar applications in the data centre.
When integrated, SD-Access and ACI exchange their groupings and provide each other an awareness of their access policies. With this knowledge, each of the domains can map user groups with applications, jointly enforce policies, and block unauthorized access to applications.
In another segmentation policy integration, Cisco SD-WAN connects with SD-Access and distributes user and device groups between an organization’s campus and branches, covering them all in a seamless access fabric. Access policies defined by SD-Access now apply consistently across all the organization’s sites.
Both these policy integrations together allow uniform access controls to be applied to users, devices, and applications regardless of where they connect to the network, or are hosted and how they move between sites, or between data centre and cloud. The integrations help avoid the complex configurations and frequent changes that would be required to achieve the same objectives.
Application experience policy integration
Ensuring that users have a good quality of experience when they run applications and access data in data centres and clouds is a high priority for businesses. It has always been hard to implement it end-to-end.
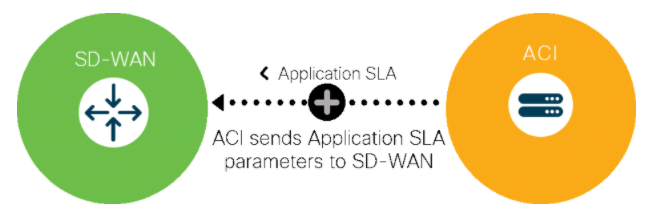
With policy integration between ACI and SD-WAN, application SLAs can be defined in the data centre and propagated automatically to SD-WAN, which can then properly prioritize the traffic as it travels to users in campus and branches. The SLA propagation can save network operators from having to define these parameters manually in SD-WAN and update them every time the application or business needs change.
Security across Domains
Security must be integrated into networks. It cannot just run at the perimeter. Integration between security and the network allows security applications and the network to work together to reduce time to prevent, detect, and mitigate threats.
Cisco’s security applications are pervasive and built-in into campus, branch, WAN, data centre, co-location centres, and cloud.
 Finland
Finland Germany
Germany Denmark
Denmark Sweden
Sweden Italy
Italy Netherlands
Netherlands Norway
Norway 























No Comments